GASEOUS EXCHANGE IN HUMAN
Human respiratory system is a series of organs responsible for taking in oxygen and expelling carbon dioxide. The primary organ of the respiratory systems is lungs. Through breathing, inhalation and exhalation, the respiratory system facilitates the exchange of gases between the air and the blood and between the blood and the body cell.

Diagram 1.1 Human respiratory system
There are difference between inhalation and exhalation in breathing process of human.
Inhalation
- External intercostal muscle contrat while intercostal muscle relax.
- Rib cage move upwards and outwards.
- Diaphragm contract and get flattens by moving down.
- Volume of thoracic cavity increases while pressure decreases.
- Atmospheric pressure is higher and force the air into the lungs.
- Air rich in oxygen is taken into the blood.
- External intercostal muscle relax while intercostal muscle contract.
- Rib cage move downwards and inwards.
- Diaphragm relax and turn into dome-shaped by moving up.
- Volume of thoracic cavity decreases while pressure increases.
- Atmospheric pressure is lower and force the air out of the lungs.
- Carbon dioxide is pushed out.

Diagram 1.2 Breathing process in human
Lung Model Activity
Structure
It is a red pigment present in red blood cells (erythrocytes). It made up of 4 polypeptide chain, called globin proteins. There are 2α and 2β chains. There are 141 and 146 amino acids in the α and β chains of haemoglobin respectively. Each of chain contains a haem group(with iron atom). The iron is the key to process oxygen. Molecules with more oxygen bound to the haem groups are brighter red. As a result, oxygenated arterial blood where the haemoglobin is carrying four oxygen molecules is bright red, while venous blood that is deoxygenated is darker red.Haemoglobin can be divided into:
- Oxyhaemoglobin- has a higher affinity for oxygen.
- Deoxyhaemoglobin- is more attracted to carbon dioxide.
Function
Haemoglobin responsible in binding and transporting oxygen from the capillaries in the lungs to all of the tissues in the body. It also plays a role in the transport of carbon dioxide from the tissues of the body back to the lungs. The diagrams shown below are the transport process of oxygen and carbon dioxide.  |
| Diagram 1.4 Oxygen pickup |
 |
| Diagram 1.5 Oxygen delivery |
 |
| Diagram 1.6 Carbon dioxide pickup |
 |
| Diagram 1.7 Carbon dioxide delivery |
Oxygen Dissociation Curve
This curve show the relationship between degree of haemoglobin saturation with oxygen at different values of pressure of oxygen.
- The loading tension of haemoglobin is about 95% because 100% saturation does not occur in natural conditions.
- Unloading tension is the tension or partial pressure at which 50% haemoglobin is saturated with oxygen.
- The curve shows sigmoid shape or "s " shape due to the cooperativity of haemoglobin binding with oxygen. The binding of first oxygen molecule to a haem group will facilitates the binding of the second and third oxygen molecules while fourth oxygen molecule is slower to bind due to the distorted shape of haemoglobin molecule.
So, let's have a look on the oxygen dissociation curve:

Based on the curve above, we can understand that:
- The steepness of curve shows oxyhaemoglobin dissociates to release oxygen.
- When the partial pressure of oxygen is high as in the pulmonary capillaries of the lungs, haemoglobin in the red blood cells has a high affinity for oxygen to form oxyhaemoglobin.
- When the partial pressure of oxygen is low as in actively respiring tissues, the oxyhaemoglobin disociates and oxygen is liberated.
The Bohr Effect
This effect is used to describe the right shift of oxygen dissociation curve. The effect can also be known as Bohr shift.
The right shif t of the oxygen dissociation curve can be caused by:
1. higher PO2
2. lower pH/ increase in hydrogen ions
3. higher temperture
4. higher DPG
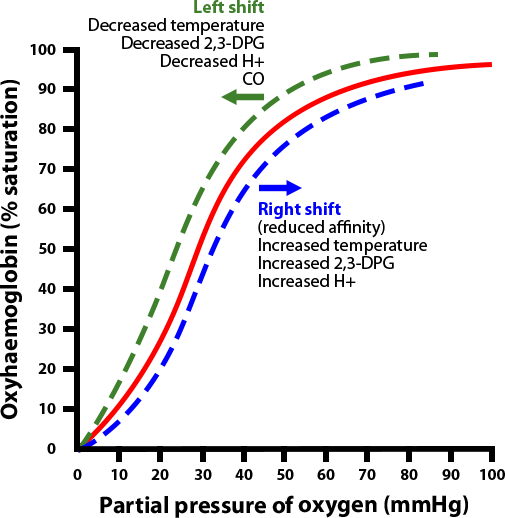
* the bohr effect can happen in actively respiring tissues during exercises.
For more understanding, please follow the link of video :
Don't forget to....
Test Your Understanding
